In today’s interconnected world, staying in touch is more important than ever, whether you’re traveling to remote locations or need to ensure communication in emergencies. While smartphones have become ubiquitous, they rely on traditional cell towers and Wi-Fi signals. But what about when you’re off the grid, far from any cell tower? This is where satellite phones come into play.
If you’re considering investing in one, you’re probably wondering, “Does a satellite phone work everywhere?” In this article, we’ll explore the key facts you need to know about satellite phones, how they work, and the limitations you may encounter. Whether you’re trekking through the wilderness or heading to a place with limited infrastructure, we’ll break down what you can expect from these devices.
What is a Satellite Phone?
Before diving into the details, let’s first understand what a satellite phone is. A satellite phone is a type of mobile phone that connects directly to satellites in orbit, rather than relying on terrestrial cell towers for communication. This allows satellite phones to function in areas where conventional cellular networks can’t reach, such as remote islands, mountainous regions, or the open ocean.
How Do Satellite Phones Work?
Satellite phones work by sending signals to satellites orbiting Earth. These satellites relay the signals to ground stations, which then route the call to its final destination. The most common types of satellite phone networks are:
- Geostationary Orbit Satellites (GEO): These satellites remain stationary relative to the Earth’s surface, offering a stable and continuous connection in some regions.
- Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEO): LEO satellites are closer to Earth and move around it, offering better coverage in certain areas, but may require more frequent handovers during communication.
Does a Satellite Phone Work Everywhere?
Now, let’s answer the central question: Does a satellite phone work everywhere? The short answer is: Not always. While satellite phones are highly reliable in many remote locations, several factors can affect their functionality.
Coverage Area
The effectiveness of a satellite phone largely depends on the coverage area provided by the satellite network it uses. Here are some key considerations:
- Global Coverage: Many satellite phone networks, such as Iridium and Globalstar, offer near-global coverage, including polar regions, oceans, and remote wilderness areas. This makes them ideal for use in regions with little to no cellular infrastructure.
- Limited Coverage in Urban Areas: In urban areas or places with dense infrastructure, satellite phone coverage might be less effective. This is because buildings, mountains, or dense foliage can obstruct the satellite’s line of sight. In cities or areas with strong cellular networks, traditional phones are often more reliable than those with mobile data.
Iridium Satellite Phones
Iridium is one of the few satellite phone providers offering truly global coverage, including the poles. With 66 low-Earth orbit satellites, it ensures connectivity even in some of the most remote regions on Earth. According to Iridium Communications, their service provides 99% global coverage, meaning there are very few areas where it doesn’t reach.
Line of Sight and Obstructions
Satellite phones require a clear line of sight to the sky to establish a stable connection with satellites. This is where the physical environment plays a critical role:
- Remote Regions: In wide-open spaces like deserts, oceans, or mountaintops, satellite phones tend to work flawlessly because there’s minimal obstruction.
- Dense Forests and Urban Areas: Thick trees, tall buildings, or mountainous terrain can block the satellite signal, causing drops in call quality or service interruptions. This is especially true in mountainous areas where the land can obstruct GEO satellites, and LEO satellites might require more handovers, leading to occasional delays or disconnections.
Battery Life and Power Needs
Satellite phones generally consume more battery than traditional mobile phones due to their reliance on satellite signals. In areas with poor satellite visibility, your phone may require more power to maintain the connection, which can cause the battery to deplete more quickly. Additionally, satellite phones typically need larger, specialized batteries that can be more challenging to recharge in remote locations.
Expert Opinion:
Dr. John Hughes, a telecommunications specialist at the University of Michigan, explains:
“Satellite phones are excellent for connectivity in remote areas, but their effectiveness depends on factors like environmental obstacles, battery life, and the satellite network’s infrastructure. While some areas are covered seamlessly, others—especially in cities—may not be ideal due to physical obstructions.”
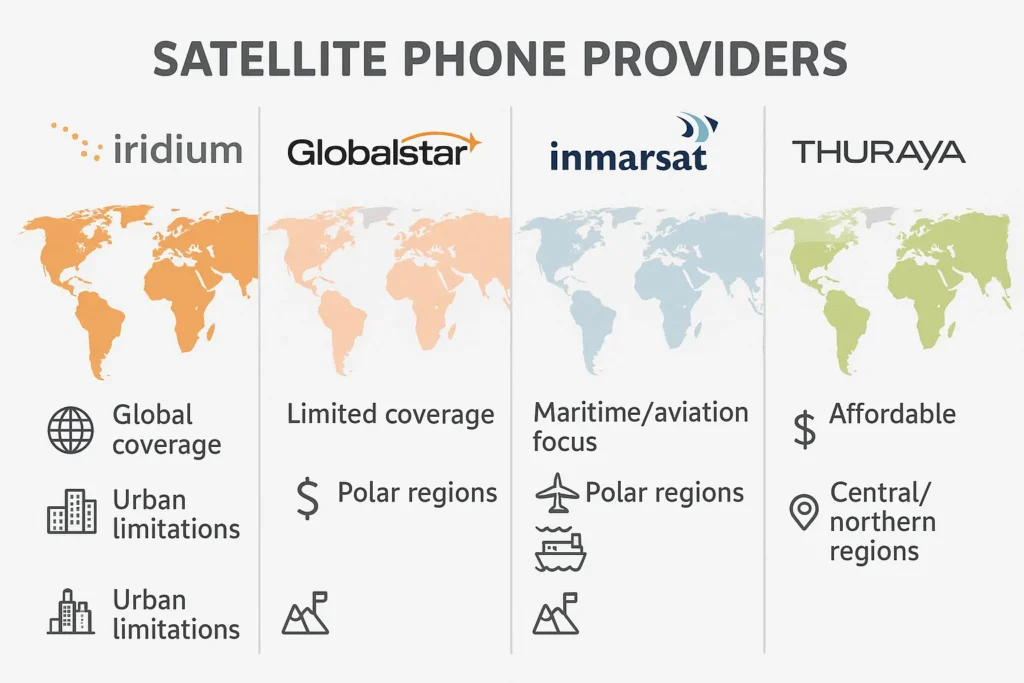
Satellite Phone Service Providers
Not all satellite phones are created equal, and different providers offer varying levels of coverage. Below are some of the top satellite phone networks, along with their comparative strengths.
1. Iridium Communications
Iridium offers global coverage, including remote areas in the Arctic and Antarctic. They utilize 66 satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), which enables them to provide near-constant service even in the most remote locations.
- Strengths: Truly global coverage, even at the poles and over oceans.
- Limitations: Not ideal in dense urban areas with tall buildings.
2. Globalstar
Globalstar provides coverage in North America, Europe, and parts of the South Pacific. However, its global coverage isn’t as comprehensive as Iridium’s.
- Strengths: Offers reliable coverage in both urban and rural areas of the United States.
- Limitations: Limited coverage in some parts of Africa and the polar regions.
3. Inmarsat
Inmarsat’s satellite network is primarily used for voice and data services for maritime and aviation applications. Its network provides a stable signal in open seas and sky, but doesn’t offer global coverage as Iridium does.
- Strengths: Excellent for maritime and aviation use.
- Limitations: Not ideal for land-based, remote travel.
4. Thuraya
Thuraya offers coverage in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, parts of Africa, and Australia. However, its coverage is less comprehensive than Iridium’s, especially in the polar regions.
- Strengths: Affordable plans and reliable in covered regions.
- Limitations: Limited coverage in remote and polar areas.
Real-World Case Study: Satellite Phone Usage in Extreme Conditions
The Case of Polar Explorers
Polar explorers often use satellite phones to communicate in some of the most remote regions of the Earth. For instance, the Arctic and Antarctic Expeditions frequently rely on Iridium’s satellite phones to stay connected with their teams and headquarters. These explorers report that Iridium’s 100% global coverage, including the polar regions, provides reliable communication even when no other form of connectivity is available.
Natural Disasters and Emergency Situations
Satellite phones have been a lifeline for disaster response teams in remote or damaged regions where traditional infrastructure is down. After the devastating 2010 Haiti earthquake, satellite phones were crucial for rescuers and aid organizations to maintain contact with local and international teams.
Expert Opinion:
Dr. Sarah Lee, an emergency management expert, says:
“In disaster zones, satellite phones are essential tools for communication when local cellular networks are destroyed. The ability to send critical information in real-time can save lives.”
Factors That Affect Satellite Phone Performance
While satellite phones can be highly reliable in many situations, several factors can affect their performance:
1. Weather Conditions
Severe weather, such as heavy rain, snowstorms, or extreme winds, can disrupt the signal; however, satellite phones generally perform better in adverse weather conditions than cell phones.
2. Geographic Location
As mentioned, a satellite phone’s signal strength is strongest when there is a clear line of sight to the sky—the more isolated or remote the area, the better the connection.
3. Satellite Network Type
Different satellite networks have varying degrees of coverage and reliability. LEO satellites provide faster connections but may require more handovers, while GEO satellites provide a more stable connection but may struggle in regions with dense obstructions.
Conclusion: Does a Satellite Phone Work Everywhere?
In conclusion, satellite phones operate effectively almost everywhere, but their performance can be influenced by factors such as network coverage, environmental obstructions, and satellite positioning. Iridium stands out for offering truly global coverage, including the polar regions, making it the most reliable option for those venturing into the most isolated areas.
If you plan to travel to remote areas, embark on an adventure, or require reliable communication in emergencies, a satellite phone can provide the connectivity you need. However, keep in mind the limitations when in urban areas or dense environments where physical obstructions can block the signal.
Also Read: Does 5G Use More Data Than 4G? Here’s What You Need to Know






